
Every organisation has a different array of stakeholders, whether it be customers, staff, consumers, suppliers, the Board, shareholders, clients or owners. Each of these stakeholders have different needs and expectations. For example, customers may want great service or excellent value, staff may want certainty and to be paid well for what they do, and shareholders may seek a solid return on their investment. As professionals, we are there to help balance the needs of these stakeholder groups. At the end of the day, none of these groups would exist without the need for the service or product in the first place, and no business would survive without these consumers paying for (or being funded for) these products and services.
So, why would consumers spend money with your organisation, and keep on coming back?
Customer Experience
Happy customers receive a perceived value or benefit from purchasing a product or service. A core component of receiving value and benefits is through having a positive customer experience.
Positive customer experiences drive positive emotions, brand loyalty and referrals. For companies it is also shown to increase stock prices. You enable trust in your brand by providing products and services which are timely, consistent, easy/simple, are of great value and meet needs of customers. Customer intimacy is also an important sustainable differentiator.

Two thirds of companies now compete on the basis of customer experience (and that figure is projected to increase).
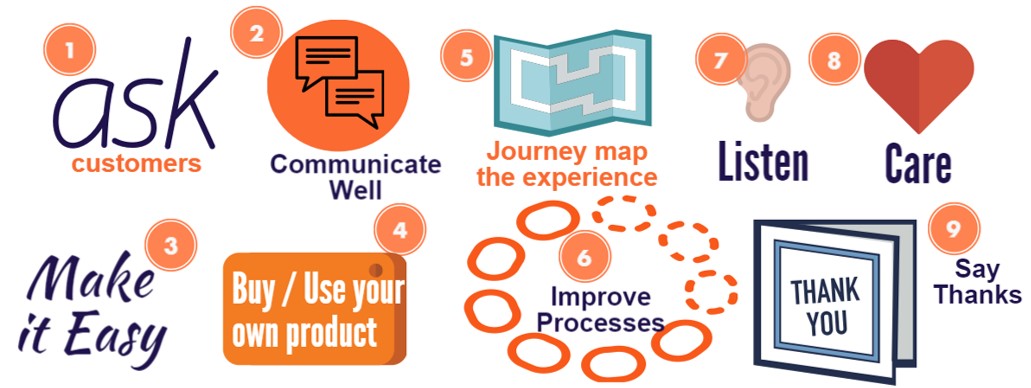
So, how do we improve customer experience?
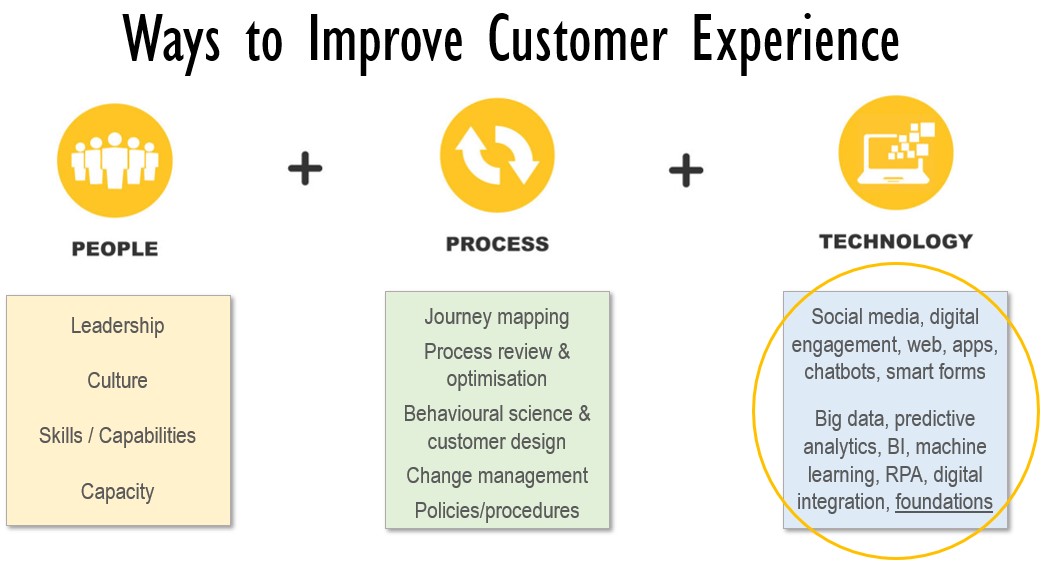
There are many ways to improve customer experience, some of which involve technology, all of which involve process change, people and leadership.
Technology is a significant enabler of customer experience but is certainly not the magic pill to address all customer experience challenges. For the perspective of the IT department and IT leader there is a need to reprioritise technology projects towards those that are geared towards providing better customer experiences. The technology department must work very closely with other areas of the organisation (such as HR, Marketing, PMO, etc) to make this happen and to ensure alignment of change.
The Approach
I believe the best approach is simply talk with people. Talk and (more importantly) listen to as many stakeholders as possible to find out what they do, how they do it, and what their challenges and pain points are.
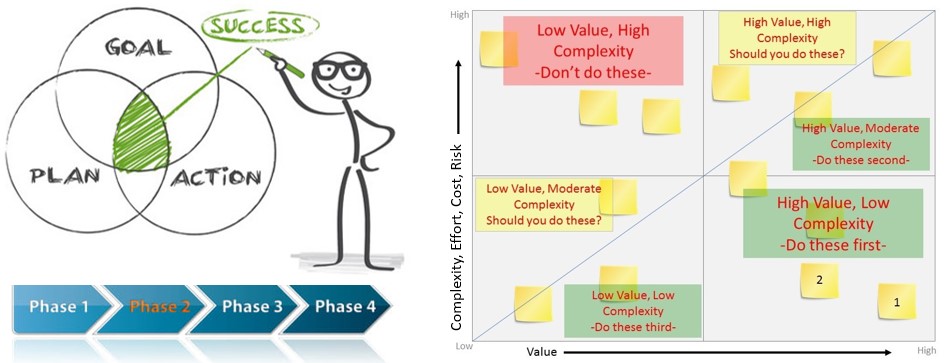
Synthesize this information, along with research, experience and best practice to devise a plan, ensuring that the end goals and objectives were well defined and aligned to Corporate Strategy.
This should be broken into phases and prioritised based on costs, value for money, effort, complexity and risk.
In Summary
- Identify the end goals & objectives. What are the problems you are trying to solve?
- Liaise with key internal and external stakeholders
- Develop a plan (aligned with corporate strategy)
that includes:
- An integrated approach to encompass people, process and technology
- Customer experience (mostly external) and operational excellence (mostly internal)
- Prioritisation of initiatives based on value, cost, risk, complexity, effort.
- Identify low hanging fruit, quick wins, etc. Celebrate the wins. Be agile. Fail/learn fast.
- Leadership, leadership, leadership (plus teamwork and accountability)
- “Sell” the plan. It’s all about the people. Communicate as one with simplicity and meaning.
- Change management. Answer the “what’s in it for me” question to improve change acceptance
- Measure benefits and success. Reassess the plan and priorities regularly.
“Train people well enough so they can leave, treat them well enough so they don’t want to“
Richard Branson
